Demo¶
Here are a few examples of the use-cases to use Greppo. The scripts are provided here along with their output screenshot.
To serve the app, run the following command on the terminal:
$ greppo serve app.py
1. Visualizing overlay layers with a base layer¶
Script - app.py¶
from greppo import app
import geopandas as gpd
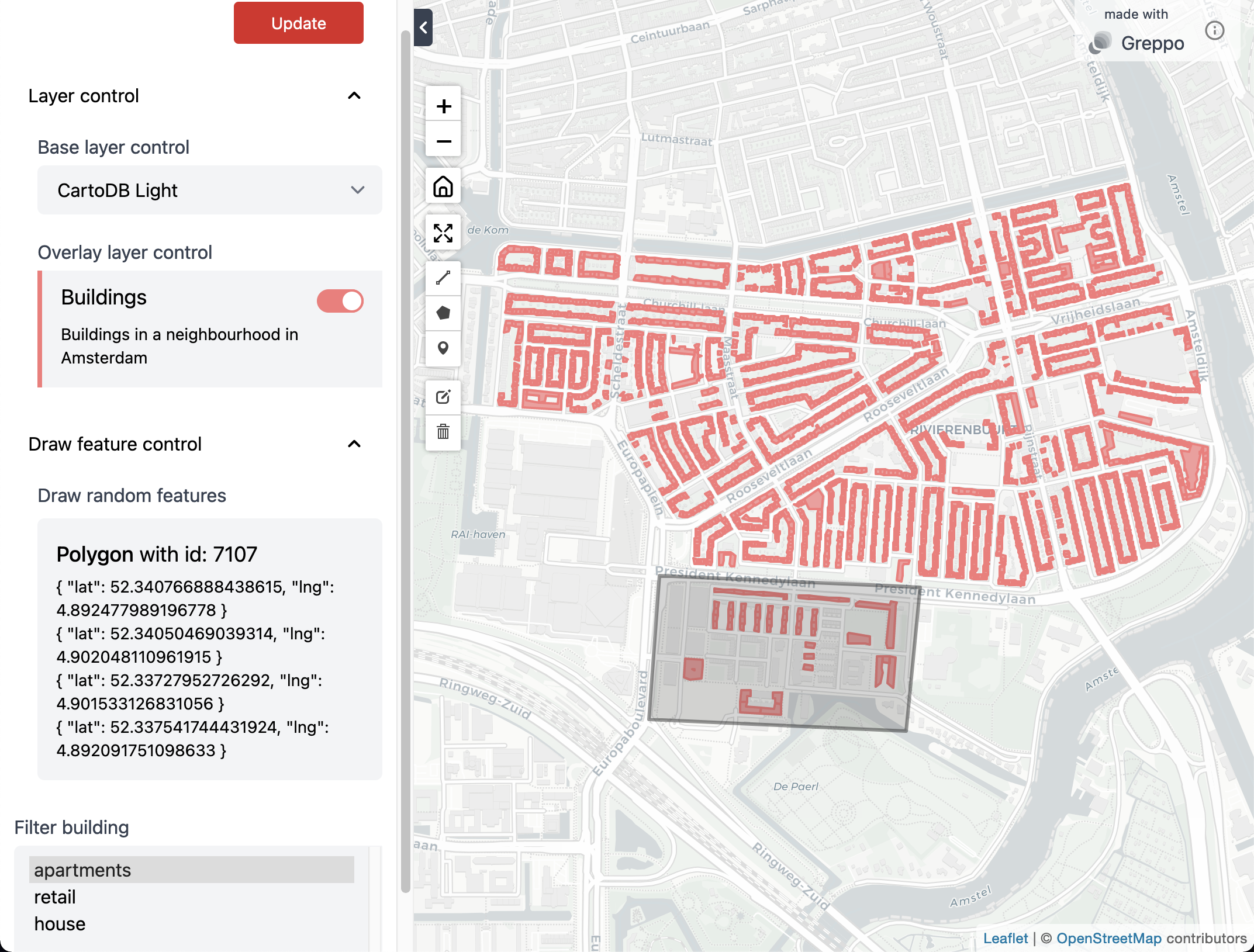
app.base_layer(
name="CartoDB Light",
visible=True,
url="https://cartodb-basemaps-a.global.ssl.fastly.net/light_all/{z}/{x}/{y}@2x.png",
subdomains=None,
attribution='© <a target="_blank" href="http://osm.org/copyright">OpenStreetMap</a> contributors',
)
buildings_gdf = gpd.read_file("./data/buildings.geojson")
app.overlay_layer(
buildings_gdf,
name="Buildings",
description="Buildings in a neighbourhood in Amsterdam",
style={"fillColor": "#F87979"},
visible=True,
)
Browser - localhost:8000/¶
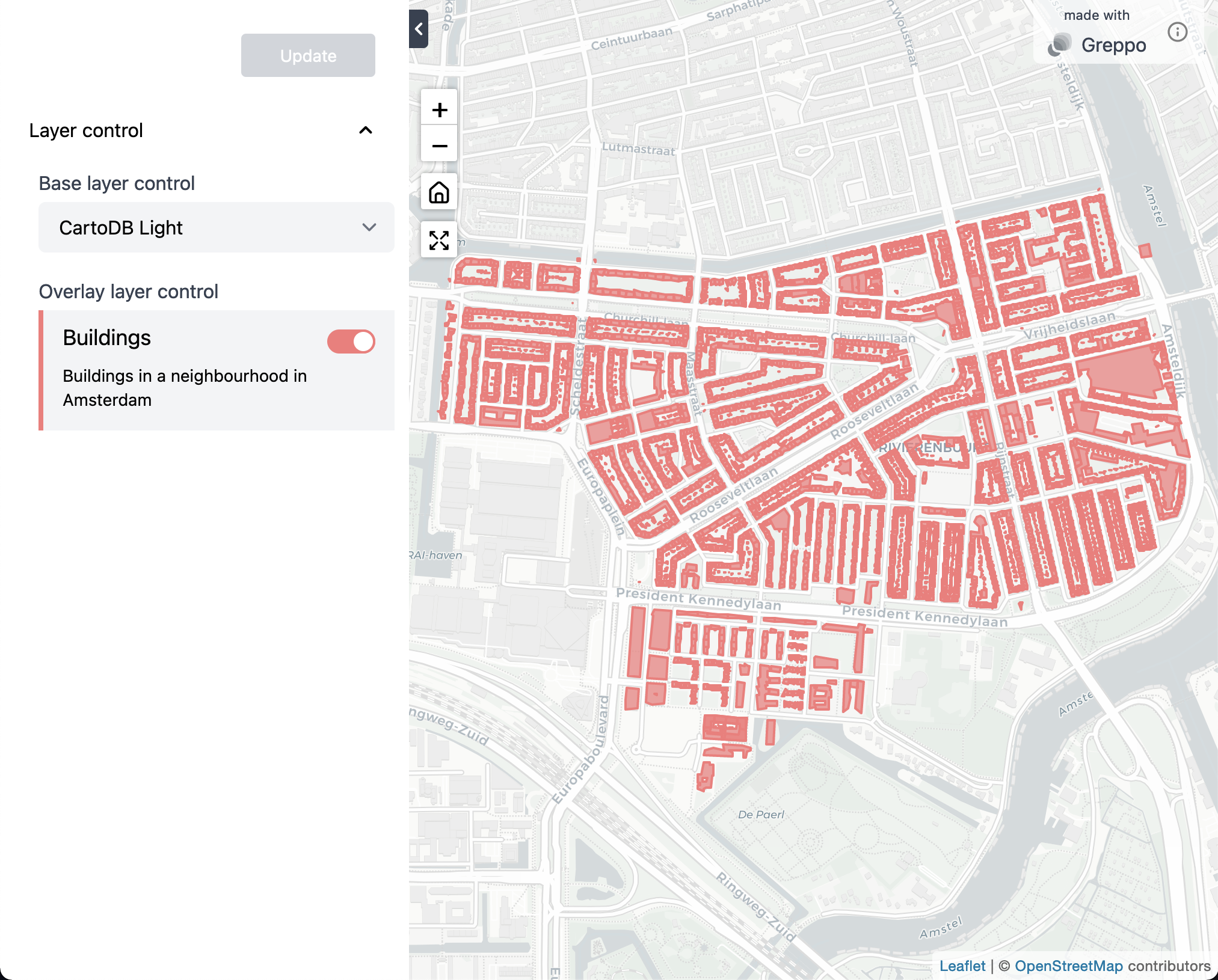
2. Adding a multiselect component to filter the geodataframe and add a draw feature¶
Script - app.py¶
from greppo import app
import geopandas as gpd
app.base_layer(
name="CartoDB Light",
visible=True,
url="https://cartodb-basemaps-a.global.ssl.fastly.net/light_all/{z}/{x}/{y}@2x.png",
subdomains=None,
attribution='© <a target="_blank" href="http://osm.org/copyright">OpenStreetMap</a> contributors',
)
buildings_gdf = gpd.read_file("./data/buildings.geojson")
filter_select = app.multiselect(name="Filter building", options=["apartments", "retail", "house"], default=["house"])
buildings_gdf_filtered = buildings_gdf[buildings_gdf.building == filter_select.get_value()[0]]
app.overlay_layer(
buildings_gdf_filtered,
title="Buildings",
description="Buildings in a neighbourhood in Amsterdam",
style={"fillColor": "#F87979"},
visible=True,
)
# Initialize an empty GeoDataFrame for referencing the draw features.
draw_features = gpd.GeoDataFrame()
draw_feature_input = app.draw_feature(
name="Draw random features", features=draw_features
)
Browser - localhost:8000/¶